The Get-ChildItem cmdlet, along with filtering parameters such as -Filter, -Include, and -Exclude provides a powerful way to search and retrieve specific files and folders within your directory.
The following methods show how you can do it.
Method 1: Using the -Filter parameter to get files with a specific extension
Get-ChildItem -Filter "*.txt"This example will get all files with the .txt extension in the current directory.
Method 2: Using -Filter parameter to filter directories
Get-ChildItem -Directory -Filter "L*"This example will get all directories that start with the letter “L” in the current directory.
The following examples show how you can use these methods.
How to use Get-ChildItem with Filter in PowerShell
You can use the Get-ChildItem cmdlet in PowerShell to retrieve files and folders from the specified directory and use the -Filter parameter to specify the condition.
# specify the directory path $folderPath = "C:\temp\" # get all files with a specific extension using the -Filter parameter $files = Get-ChildItem -Path $folderPath -Filter "*.txt" Write-Output $files
Output:
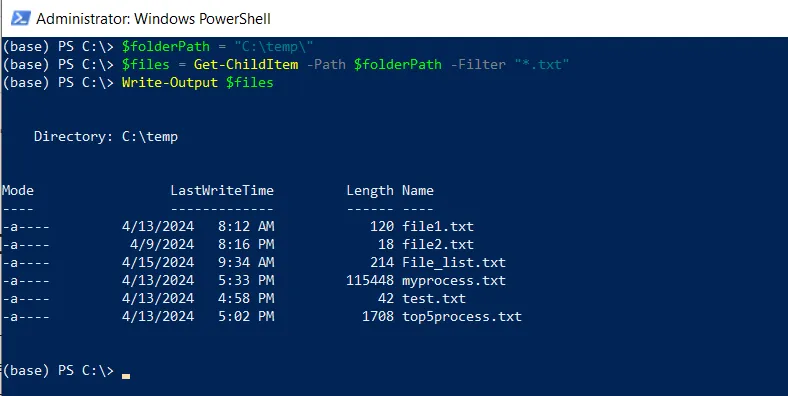
In this script, we define a variable $folderPath that stores the directory path from where you want to retrieve the .txt extension file.
We then use the Get-ChildItem cmdlet to specify the folder path $folderPath to retrieve only files with extension .txt using the -Filter parameter.
For example, “*.txt” matches all files with the .txt extension. In the filter pattern, you can also use wildcard characters like * or ?.
Finally, we use the Write-Output cmdlet in PowerShell to output the .txt files to the console.
After running the PowerShell script, it outputs the files with a .txt extension.
How to Use Get-ChildItem with Filter to Filter Directories
You can use the Get-ChildItem cmdlet in PowerShell with the -Filter parameter to filter the directories based on a specified filter.
# specify the directory path $folderPath = "C:\temp\" # get all directories that start with the letter "L" $folders = Get-ChildItem -Path $folderPath -Directory -Filter "L*" Write-Output $folder
Output:
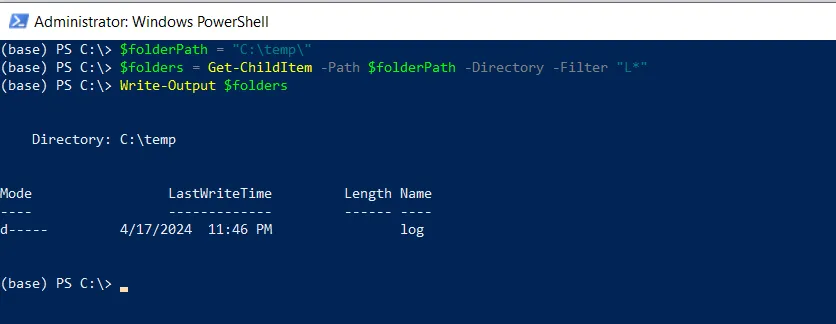
In this script, we define a variable $folderPath that stores the folder path.
We then use the Get-ChildItem cmdlet with the -Filter parameter to specify the filter pattern “L*“, which means getting all directories that start with the letter “L” and storing them in the $folders variable.
Finally, we use the Write-Output cmdlet to output the folder path to the console.
After running the PowerShell script, it retrieves the list of directories that start with the letter “L“.
Conclusion
I hope the above article on using the Get-ChildItem with Filter parameter in PowerShell is helpful to you.
You can find more topics about Active Directory tools and PowerShell basics on the ActiveDirectoryTools home page.