You can use the Where-Object cmdlet alongside regex patterns for filtering objects in PowerShell.
The following method shows how you can do it with syntax.
Method 1: Using Where-Object with Regex
$files = Get-ChildItem -Path "C:\temp\log\"
$txtFiles = $files | Where-Object { $_.Name -match "\.txt$" }
Write-Output $txtFilesThis example will filter files with the .txt extension and display a filtered list of .txt files.
The following example shows how you can use this method.
Using Where-Object with Regex in PowerShell
You can use the Where-Object cmdlet in conjunction with the -match operator to filter files with the .txt extension.
# Get list of files in directory
$files = Get-ChildItem -Path "C:\temp\log\"
# Filter the list to get only files with a .txt extension using regex
$txtFiles = $files | Where-Object { $_.Name -match "\.txt$" }
# Output the .txt files
Write-Output $txtFiles
Output:
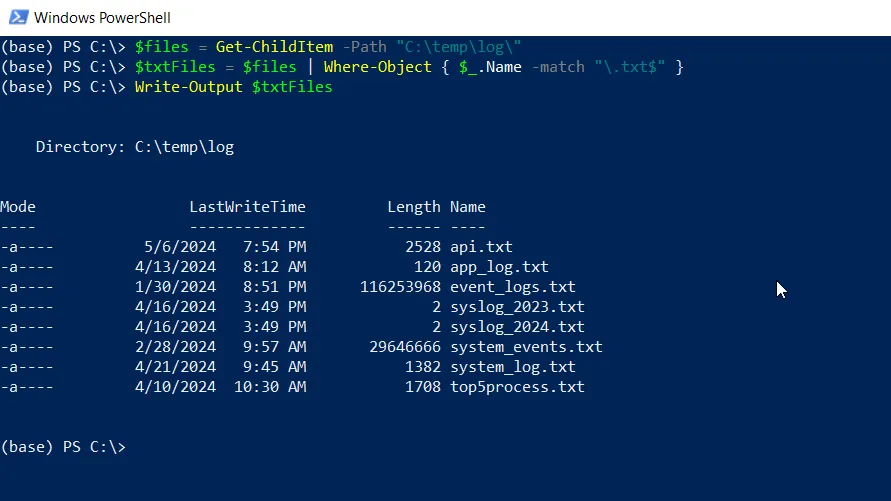
In this example, the Get-ChildItem cmdlet retrieves a list of files in the C:\temp\log\ directory and stores it in the $files variable.
The Where-Object cmdlet filters the $files array and uses the regex patterns "\.txt$" to each object’s Name property. The -match operator checks if the Name property matches the specified regex pattern and stores the result in $txtFiles.
Finally, the filtered list of .txt files is displayed using the Write-Output cmdlet
Conclusion
I hope the above article on using Where-Object with regex pattern in PowerShell is helpful to you.
You can find more topics about Active Directory tools and PowerShell basics on the ActiveDirectoryTools home page.