There are several ways in PowerShell to get file extensions.
The following methods show how you can do it.
Method 1: Using the Split-Path and Split() method
# specify the file path
$filePath = "C:\temp\log\my_log.txt"
# Get the filename with extension
$fileNameWithExtension = Split-Path -Path $filePath -Leaf
# Split the filename and extension using the Split() method
$fileExtension = $fileNameWithExtension.Split(".")[1]
# output the file extension
Write-Output $fileExtensionThis example uses the Split-Path cmdlet and Split() method to extract the file extension and output to the console.
Method 2: Using the [System.IO.Path] .Net class
# specify the file path
$filePath = "C:\temp\log\my_log.txt"
# Get the extension
$fileExtension = [System.IO.Path]::GetExtension($filePath)
# output the file extension
Write-Output $fileExtensionThis example uses the [System.IO.Path] .Net class and its method GetExtension() to get file extension.
Method 3: Using the Get-ChildItem cmdlet
# specify the file path
$filePath = "C:\temp\log\my_log.txt"
# Get the file extension
$fileExtension = (Get-ChildItem -Path $filePath -File).Extension
# output the file extension
Write-Output $fileExtensionThis example uses the Get-ChildItem cmdlet to extract the file extension.
Method 4: Using the Get-Item cmdlet
# specify the file path
$filePath = "C:\temp\log\my_log.txt"
# Get the file extension
$fileExtension = (Get-Item -Path $filePath).Extension
# output the file extension
Write-Output $fileExtensionThis example uses the Get-Item cmdlet to extract the file extension.
The following examples show how to use these methods to get a file extension.
Get File Extension Using Split-Path and Split() in PowerShell
You can use the Split-Path cmdlet to get the filename with extension using its -Leaf parameter and then use the Split() method to extract the file extension.
# specify the file path
$filePath = "C:\temp\log\my_log.txt"
# Get the filename with extension
$fileNameWithExtension = Split-Path -Path $filePath -Leaf
# Split the filename and extension using the Split() method
$fileExtension = $fileNameWithExtension.Split(".")[1]
# output the file extension
Write-Output $fileExtension
Output:
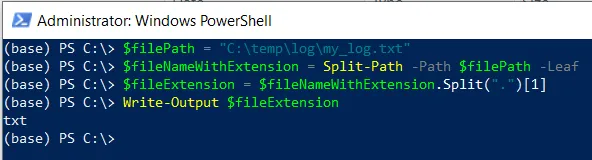
In this script, the $filePath variable stores the path to the file. The Split-Path cmdlet in PowerShell gets the filename with extension using its -Leaf parameter and stores it in the $fileNameWithExtension variable.
Finally, we call the Split() method over the $fileNameWithExtension variable to extract the file extension and output to the console using the Write-Output cmdlet.
The script will extract and display the file extension “txt” on the console.
Get File Extension Using [System.IO.Path] Class
You can use the [System.IO.Path] .NET class to get the file extension using its GetExtension() method.
# specify the file path $filePath = "C:\temp\log\my_log.txt" # Get the extension $fileExtension = [System.IO.Path]::GetExtension($filePath) # output the file extension Write-Output $fileExtension
Output:
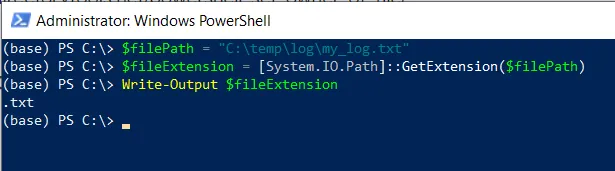
In this script, the $filePath variable stores the path to the file. We call the [System.IO.Path] .NET class GetExtension() method to get the file extension and store it in the $fileExtension variable.
Finally, we use the Write-Output cmdlet to output file extension to the console.
The script will extract and display the file extension “txt” on the console.
Get File Extension Using the Get-ChildItem in PowerShell
Another way to get file extension is by using the Get-ChildItem cmdlet in PowerShell. It uses the Extension property of the file object to get the file extension.
# specify the file path $filePath = "C:\temp\log\my_log.txt" # Get the file extension $fileExtension = (Get-ChildItem -Path $filePath -File).Extension # output the file extension Write-Output $fileExtension
Output:
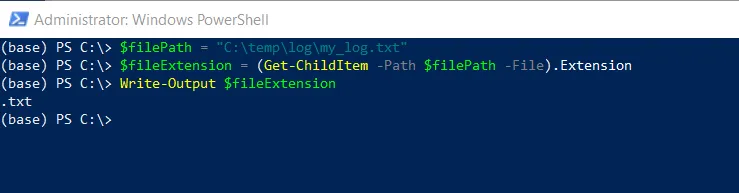
In this script, the $filePath variable stores the path to the file. The Get-ChildItem cmdlet uses the -Path variable to specify the file path and get the file object. It then uses the Extension property of the file object and stores it in the $fileExtension variable.
Finally, we use the Write-Output cmdlet to output a file extension to the console.
The script will extract and display the file extension “txt” on the console.
Get File Extension Using the Get-Item in PowerShell
You can get file extension by using the Get-Item cmdlet in PowerShell. It uses the Extension property of the file object to get the file extension.
# specify the file path $filePath = "C:\temp\log\my_log.txt" # Get the file extension $fileExtension = (Get-Item -Path $filePath).Extension # output the file extension Write-Output $fileExtension
Output:
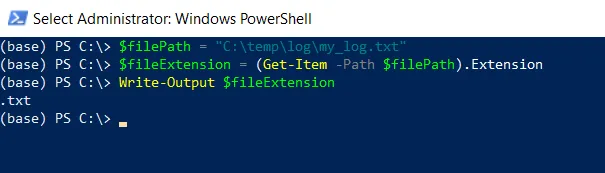
In this script, the $filePath variable stores the path to the file. The Get-Item cmdlet uses the -Path variable to specify the file path and get the file object. It then uses the Extension property of the file object and stores it in the $fileExtension variable.
Finally, we use the Write-Output cmdlet to output a file extension to the console.
The script will extract and display the file extension “.txt” on the console.
Conclusion
I hope the above article on how to get a file extension in PowerShell is helpful to you.
You can find more topics about Active Directory tools and PowerShell basics on the ActiveDirectoryTools home page.